122 lines
6.4 KiB
Markdown
122 lines
6.4 KiB
Markdown
# 1.1 Installation
|
|
|
|
## Three ways to install Go
|
|
|
|
There are many ways to configure the Go development environment on your computer, and you can choose whichever one you like. The three most common ways are as follows.
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Official installation packages.
|
|
- The Go team provides convenient installation packages in Windows, Linux, Mac and other operating systems. This is probably the easiest way to get started.
|
|
- Install it yourself from source code.
|
|
- Popular with developers who are familiar with Unix-like systems.
|
|
- Using third-party tools.
|
|
- There are many third-party tools and package managers for installing Go, like apt-get in Ubuntu and homebrew for Mac.
|
|
|
|
In case you want to install more than one version of Go on a computer, you should take a look at a tool called [GVM](https://github.com/moovweb/gvm). It is the best tool I've seen so far for accomplishing this task, otherwise you'd have to deal with it yourself.
|
|
|
|
## Install from source code
|
|
|
|
Because some parts of Go are written in Plan 9 C and AT&T assembler, you have to install a C compiler before taking the next step.
|
|
|
|
On a Mac, if you have installed Xcode, you already have the compiler.
|
|
|
|
On Unix-like systems, you need to install gcc or a similar compiler. For example, using the package manager apt-get (included with Ubuntu), one can install the required compilers as follows:
|
|
|
|
`sudo apt-get install gcc libc6-dev`
|
|
|
|
On Windows, you need to install MinGW in order to install gcc. Don't forget to configure your environment variables after the installation has completed.( ***Everything that looks like this means it's commented by a translator: If you are using 64-bit Windows, you should install the 64-bit version of MinGW*** )
|
|
|
|
At this point, execute the following commands to clone the Go source code and compile it.( ***It will clone the source code to your current directory. Switch your work path before you continue. This may take some time.*** )
|
|
|
|
git clone https://go.googlesource.com/go
|
|
cd go/src
|
|
./all.bash
|
|
|
|
A successful installation will end with the message "ALL TESTS PASSED."
|
|
|
|
On Windows, you can achieve the same by running `all.bat`.
|
|
|
|
If you are using Windows, the installation package will set your environment variables automatically. In Unix-like systems, you need to set these variables manually as follows. ( ***If your Go version is greater than 1.0, you don't have to set $GOBIN, and it will automatically be related to your $GOROOT/bin, which we will talk about in the next section***)
|
|
|
|
export GOROOT=$HOME/go
|
|
export GOBIN=$GOROOT/bin
|
|
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin
|
|
|
|
If you see the following information on your screen, you're all set.
|
|
|
|
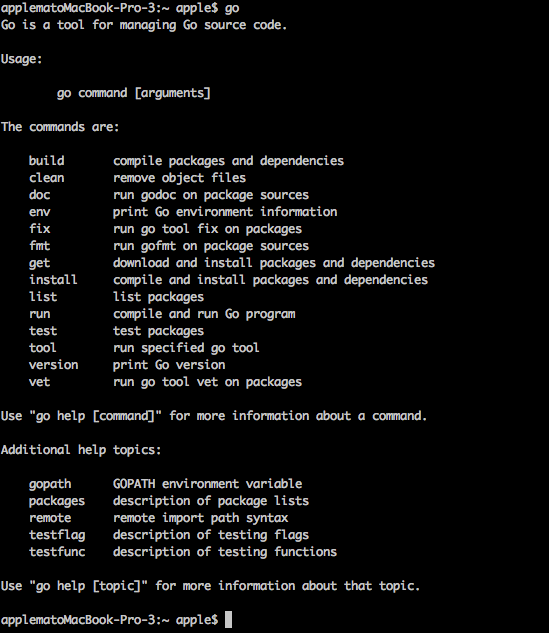
|
|
|
|
Figure 1.1 Information after installing from source code
|
|
|
|
Once you see the usage information of Go, it means you have successfully installed Go on your computer. If it says "no such command", check that your $PATH environment variable contains the installation path of Go.
|
|
|
|
## Using the standard installation packages
|
|
|
|
Go has one-click installation packages for every supported operating system. These packages will install Go in `/usr/local/go` (`c:\Go` in Windows) by default. Of course this can be modified, but you also need to change all the environment variables manually as I've shown above.
|
|
|
|
### How to check if your operating system is 32-bit or 64-bit?
|
|
|
|
Our next step depends on your operating system type, so we have to check it before we download the standard installation packages.
|
|
|
|
If you are using Windows, press `Win+R` and then run the command tool. Type the `systeminfo` command and it will show you some useful system information. Find the line that says "system type" -if you see "x64-based PC" that means your operating system is 64-bit, 32-bit otherwise.
|
|
|
|
I strongly recommend downloading the 64-bit package if you are a Mac user, as Go no longer supports pure 32-bit processors on Mac OSX.
|
|
|
|
Linux users can type `uname -a` in the terminal to see system information.
|
|
A 64-bit operating system will show the following:
|
|
|
|
<some description> x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
|
|
// some machines such as Ubuntu 10.04 will show as following
|
|
x86_64 GNU/Linux
|
|
|
|
32-bit operating systems instead show:
|
|
|
|
<some description> i686 i686 i386 GNU/Linux
|
|
|
|
### Mac
|
|
|
|
Go to the [download page](https://golang.org/dl/), choose `go1.4.2.darwin-386.pkg` for 32-bit systems and `go1.4.2.darwin-amd64.pkg` for 64-bit systems. Going all the way to the end by clicking "next", `~/go/bin` will be added to your system's $PATH after you finish the installation. Now open the terminal and type `go`. You should see the same output shown in figure 1.1.
|
|
|
|
### Linux
|
|
|
|
Go to the [download page](https://golang.org/dl/), choose `go1.4.2.linux-386.tar.gz` for 32-bit systems and `go1.4.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz` for 64-bit systems. Suppose you want to install Go in the `$GO_INSTALL_DIR` path. Uncompress the `tar.gz` to your chosen path using the command `tar zxvf go1.4.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz -C $GO_INSTALL_DIR`. Then set your $PATH with the following: `export PATH=$PATH:$GO_INSTALL_DIR/go/bin`. Now just open the terminal and type `go`. You should now see the same output displayed in figure 1.1.
|
|
|
|
### Windows
|
|
|
|
Go to the [download page](https://golang.org/dl/), choose `go1.4.2.windows-386.msi` for 32-bit systems and `go1.4.2.windows-amd64.msi` for 64-bit systems. Going all the way to the end by clicking "next", `c:/go/bin` will be added to `path`. Now just open a command line window and type `go`. You should now see the same output displayed in figure 1.1.
|
|
|
|
## Use third-party tools
|
|
|
|
### GVM
|
|
|
|
GVM is a Go multi-version control tool developed by a third-party, like rvm for ruby. It's quite easy to use. Install gvm by typing the following commands in your terminal:
|
|
|
|
bash < <(curl -s -S -L https://raw.github.com/moovweb/gvm/master/binscripts/gvm-installer)
|
|
|
|
Then we install Go using the following commands:
|
|
|
|
gvm install go1.4.2
|
|
gvm use go1.4.2
|
|
|
|
After the process has finished, you're all set.
|
|
|
|
### apt-get
|
|
|
|
Ubuntu is the most popular desktop release version of Linux. It uses `apt-get` to manage packages. We can install Go using the following commands.
|
|
|
|
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gophers/go
|
|
sudo apt-get update
|
|
sudo apt-get install golang-stable
|
|
|
|
### Homebrew
|
|
|
|
Homebrew is a software management tool commonly used in Mac to manage packages. Just type the following commands to install Go.
|
|
|
|
brew install go
|
|
|
|
## Links
|
|
|
|
- [Directory](preface.md)
|
|
- Previous section: [Go environment configuration](01.0.md)
|
|
- Next section: [$GOPATH and workspace](01.2.md)
|